Pascal - Decision Making
Decision making structures require that the programmer specify one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements to be executed if the condition is determined to be true, and optionally, other statements to be executed if the condition is determined to be false.
Following is the general from of a typical decision making structure found in most of the programming languages:
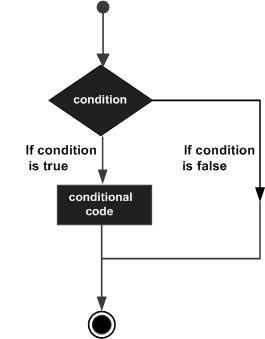
Pascal programming language provides following types of decision making statements. Click the following links to check their detail.
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| if - then statement | An if - then statement consists of a boolean expression followed by one or more statements. |
| If-then-else statement | An if - then statement can be followed by an optional else statement, which executes when the boolean expression is false. |
| nested if statements | You can use one if or else if statement inside another if or else if statement(s). |
| case statement | A case statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values. |
| case - else statement | It is similar to the if-then-else statement. Here an else term follows the case statement. |
| nested case statements | You can use one case statement inside another case statement(s). |